Visual Basic 6 stores its code in the form of module that makes your program more structured. So its very important to learn about it.
Before you start
Its recommended that you first have the concepts of scope, procedure,functions and multiple forms. The following lessons are helpful.
What is a module?
Module is a separate code file in Visual Basic that contains procedures and declarations.
Your entire VB6 program code does not come line by line. Instead they are separated in code files called modules, each of them is separated into procedures. Thus your VB6 program becomes well structured which is the key part of developing Visual Basic applications.
Form Module
The complete code including procedures and declarations part of a form is referred to as the form module.
Advantages of a BAS module
When the problem is large, its better to break it down into smaller parts to make it easy.
Problem Focus
Each function or sub should be focused on solving one problem, in a reliable and efficient manner. This keeps your bug hunting to a minimum, since your functions are only performing one function.
Code Reuse
Once you have a solidly function piece of code, that sub or function can be called from anywhere, with a single reference.
Time & Effort
No more re-writing the same code repeatedly, both in the current project as well as future projects.
Accessibilty
Public procedures can be called from anywhere in your project.
How to add a Standard BAS module to the current project?
Project -> Add Module. Click Project menu from the menu bar and select add module.
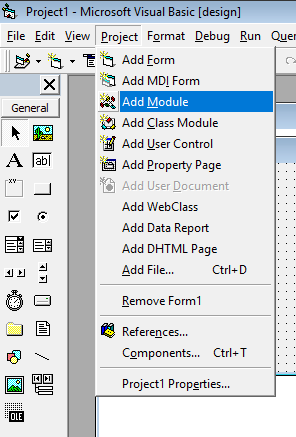
A separate project file with the .bas extension is saved on your hard disk as soon as you add a standard module to your current project. You can change the Name property of your newly added standard module from the properties window. Choose a meaningful name, it will benefit you while writing the code.
The modules are shown in project explorer window:
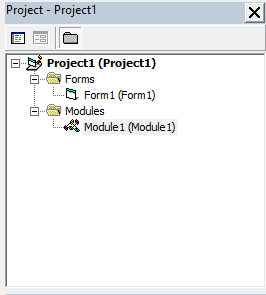
Contents of the standard module
- Procedure definitions
- Variable, type and constant declarations.
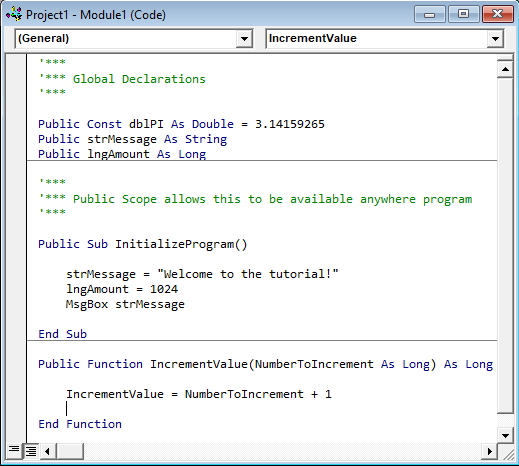
The variables and constants declared using the Public keyword in the Declrations section of the module are global, accessible from all parts of your current application.
Here is a simple example of a code inside a BAS module:
Inside the BAS Module
'Scope is Public to make it accessible from anywhere of the application
Public Sub show()
MsgBox "Welcome to the tutorial!"
MsgBox "This is a message"
MsgBox "New message!"
MsgBox "List of messages"
End Sub
Public Function increment(number As Integer) As Integer
increment = number + 1
End Function
In form1
Private Sub cmdShow_Click()
Dim num As Integer
Dim m As Integer
num = InputBox("Enter the number", "Input")
m = Module1.increment(num)
MsgBox m
Call Module1.show
End Sub
In form2
Private Sub Form_Load()
Call Module1.show
End Sub
In form3
'The show sub procedure is global
Private Sub Form_Load()
Call Module1.show
End Sub
QuickHint
BAS modules are especially useful in large projects. So if you’re developing a big VB6 application, make use of them.
